HERS Ratings & Energy Code

The HERS Rater analyzes the home’s potential energy performance using an approved simulation program and then completes both on-site inspections and diagnostic tests before issuing the home’s HERS Score and Program Tier level. The rater conducts computer modeling of your home plans to determine the estimated energy usage. If necessary, recommendations are made to help the home meet the standards of the Massachusetts Residential New Construction Program. For homes that choose a prescriptive path a HERS Rater will help identify which measures must be present.
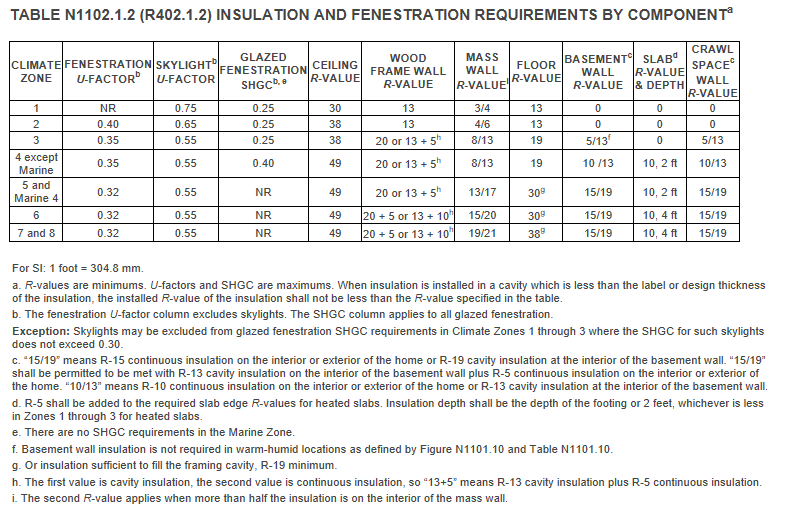
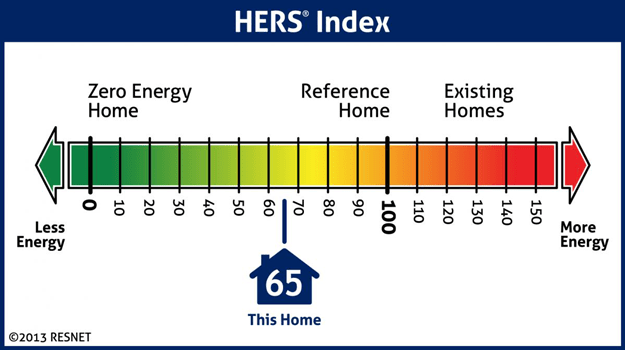
The Massachusetts Building Code requires that all new residential buildings that are three stories or less must achieve a targeted HERS Index Score as verified by a certified RESNET Home Energy Rater. The HERS Index Score is driven by the size of the home. Residential buildings that are less than 3,000 sq. ft. must have a HERS Index Score or 70 or less. Homes that are larger than 3,000 sq. ft. must have a HERS Index Score of 65 or less. The code requires that in addition to the HERS Index Score the rater must complete the ENERGY STAR Qualified Homes Thermal Bypass Inspection Checklist. New residential construction must use the performance-based approach, but residential renovations and most commercial buildings may instead opt to follow a ‘prescriptive’ route that specifies a set of minimum energy efficiency requirements for different building materials and systems. In the commercial case these add up to approximately a 20% improvement over the base code. Many of these changes have been endorsed by the federal Department of Energy and are likely to be incorporated into the commercial chapter of the next International Energy Conservation Code (IECC) in 2015.